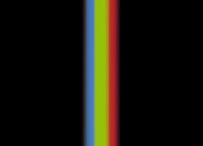| |
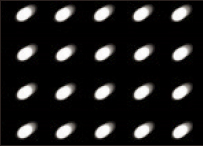
This is an inevitable type of aberration when using spherical lenses. Differences occur between the light in the center of the lens and the light at the edge of the lens, creating a halo-like blur. |
|
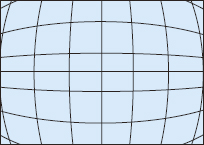
This type of distortion occurs at the edge of lenses designed to correct for spherical aberration. The name "coma" is used because the blur caused by this aberration looks like a comet's tail. |
|
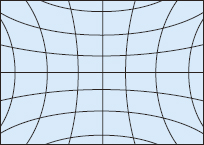
This type of aberration is caused by the lens used to correct spherical and coma aberrations. It occurs when the lens shifts from the optical axis, causing points on the edge of the lens to become either elliptical or linear. |
|
Based on the same principle as a prism breaking light into a rainbow spectrum, these aberrations cause color shifts. They are seen especially in telephoto lenses and increase as the power of the lens increases. |
|